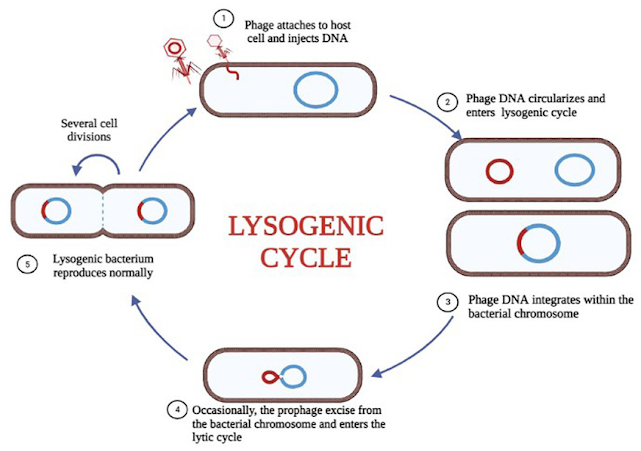
Lysogeny
Lysogeny:-
- Not all viruses multiply by the lytic cycle of reproduction.
- Certain viruses remain active within their host cells for a long period without replicating.
- This cycle is called the lysogenic cycle.
- The viruses are called temperate viruses, or proviruses, because they do not bring death to the host cell immediately.
- In lysogeny, the temperate virus exists in a latent form within the host cell and is usually integrated into the chromosome.
- Bacteriophages that remain latent within their bacterial host cell are called prophages. This process is a key element in the recombination process known as transduction.
- An example of lysogeny occurs in HIV infection. In this case, the human immunodeficiency virus remains latent within the host T-lymphocyte.