GS - GOGAT Pathway
Fate of Ammonia:-
> What happens to the ammonia generated after nitrogen-fixation? It is protonated to form ammonium ion (NH4+) at physiological pH. Although plants can accumulate nitrate and NH4+ ions, NH4+ ions are toxic to them. Thus, it is in turn, used to synthesize amino acids in plants as follows:
(i) Reductive amination:- Here, ammonia reacts with α-ketoglutaric acid to form glutamic acid in the presence of the enzyme – glutamate dehydrogenase.
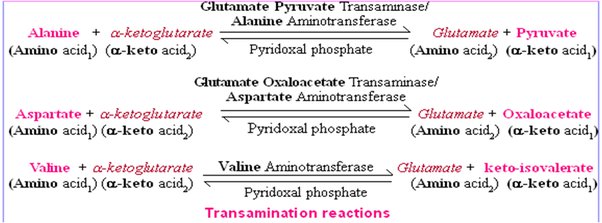
(ii) Transamination:- Here, the amino group of one amino acid is transferred to the keto group of a keto acid in the presence of the enzyme – transaminase. Asparagine and glutamine – the two most important amides in plants arise from two amino acids – aspartic acid and glutamic acid, respectively. Another NH2– radicle replaces the hydroxyl group of the acid to give an amide. The xylem then transports these amides that contain more nitrogen to different parts of the plant.
.bmp)
.bmp)