Bioassay of Auxins
Bioassay of Auxins:-
It is testing of a biological activity like growth response of a substance by employing a living material like plant or plant part. Auxin bioassay is quantitative test as it measures concentration of auxin to produce the effect and the amount of effect.
a. Avena Curvature Test:-
> The test is based upon experiments of Went (1928). 10° curvature is produced by auxin concentration of 150 µg/litre at 25° C and 90% relative humidity. The test can measure auxin upto 300 pg/litre.
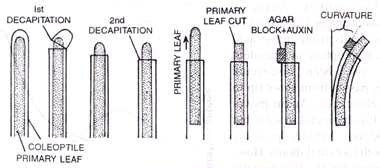
> Auxin from a shoot tip or any other plant organ is allowed to diffuse in a standard size agar block (generally 2 x 2 x 1 mm). Auxin can also be dissolved directly in agar. 15-30 mm long oat coleoptile grown in dark is held vertically over water. 1 mm tip of coleoptile is removed without injuring the primary leaf.
> After 3 hours a second decapitation is carried out for a distance of 4 mm. Primary leaf is now pulled loose and agar block supported against it at the tip of decapitated coleoptile. After 90-110 minutes, the coleoptile is found to have bent. The curvature is measured. It can also be photographed and the curvature known from shadow graph.
b. Root Growth Inhibition:-
Sterilized seeds of Cress are allowed to germinate on moist filter paper. As the roots reach a length of 1 cm or so, root lengths are measured. 50% of the seedlings are placed in a test solution while the remaining are allowed to grow over moist paper.
Lengths of the roots are measured after 48 hours. It is seen that the seedlings placed in test solution show very little root growth while root growth is normal in control seedlings.